Simulations
The Simulations feature is in private preview. For more information, reach out to Upbound.
Simulations are temporary copies of an existing control plane that allow you preview the impact of changes before applying these changes to your environment.
This feature is valuable for organizations transitioning from
traditional IaC tools like Terraform, where previewing changes with terraform plan is a standard practice. Your control plane simulation allows Crossplane to
run a composition controller and inspect how the controller behaves with
proposed changes.
Simulations provide visibility for your resource changes, including:
- New resources to create
- Existing resources to change
- Existing resources to delete
- How configuration changes propagate through the system
This can help you reduce the risk of unexpected behavior based on your changes.
This guide provides instructions for using the up ctp simulate command and the
Simulation API to test changes in your control plane.
Prerequisites
- The Upbound CLI installed
- An Upbound account with the Simulations feature enabled
- kubectl installed
Deploy a base control plane
This example uses a control plane that runs a nop provider to illustrate how
the simulations feature works.
Clone the example repository:
git clone https://github.com/upbound/no-op-sim.git && cd no-op-sim
Login to your Upbound account in the CLI:
up login --account=<your_upbound_account>
Run the project in a control plane:
up project run
Set your context to the control plane you just created:
up ctx ./noop
Deploy the example XR to create your initial resources:
kubectl apply -f examples/noop/example-xr.yaml
Run a simulation
First, change your control plane context to the group level of the running
control plane. For example, if your context is your running control plane, use
the up ctx command to switch to the group level.
up ctx ..
Next, make a change in the examples/noop/example-xr.yaml file in the project.
In this example, comment out the first ultimateAnswer and uncomment the
correct value assignment.
apiVersion: customer.upbound.io/v1alpha1
kind: XNoOp
metadata:
name: example
namespace: default
spec:
compositionRef:
name: noops.customer.upbound.io
parameters:
ultimateQuestion: "What is the meaning of life, the universe, and everything?"
#ultimateAnswer: 41
ultimateAnswer: 42
Save this change and run your simulation. The up ctp simulate command creates
a simulation of the base control plane and applies the changes found in your
changed resource directory into the mock control plane.
up alpha ctp simulate noop --changeset=./examples/noop/example-xr.yaml --complete-after=60s --terminate-on-finish
Your command line returns a summary of the resources created, modified, or deleted for each resource affected:
Simulation "noop-6wqg9" created
▄ [1/5]: Waiting for simulated control plane to start (30s)
▄ [2/5]: Waiting for simulated control plane to start (30s)
✓ [3/5]: Waiting for simulation to complete
▀ [4/5]: Computing simulated differences (0s)
✓ [4/5]: Computing simulated differences
▀ [5/5]: Terminating simulation (0s)
✓ [5/5]: Terminating simulation
Simulation: 0 resources added, 3 resources changed, 0 resources deleted
[~] XNoOp.customer.upbound.io/v1alpha1 example
└─[~] spec.parameters.ultimateAnswer
├─[-] 41
└─[+] 42
[~] Function.pkg.crossplane.io/v1 crossplane-contrib-function-auto-ready
└─[~] metadata.annotations
├─[-] <nil>
└─[+] map[]
[~] Function.pkg.crossplane.io/v1 upbound-noopnop-function
└─[~] metadata.annotations
├─[-] <nil>
└─[+] map[]
Simulations API
When you create a simulation in Upbound, you interact with the Spaces API
simulations endpoint. The Simulations endpoint has three key fields:
spec.controlPlaneNamespec.completionCriteriaspec.desiredState
controlPlaneName
The controlPlaneName field specifies the base control plane. You must specify
the control plane name to create the correct simulation.
completionCriteria
The completionCriteria field specifies how Spaces should
determine when the simulation is complete. When the simulation meets the
criteria you set, Upbound sets the simulated control plane's desired state to
Complete.
The completionCriteria is list of criteria that determines when a simulation
should complete. We currently only support type: Duration, a string that
indicates the duration of how long a simulation should run for in seconds.
apiVersion: spaces.upbound.io/v1alpha1
kind: Simulation
metadata:
name: simulation
namespace: default
spec:
controlPlaneName: source
desiredState: AcceptingChanges
completionCriteria:
- type: Duration
duration: 90s
When you start a simulation, you can add the complete-after flag to explicitly
define the completionCriteria of your simulation:
up alpha ctp simulate noop --changeset=./examples/noop/example-xr.yaml --complete-after=30s --terminate-on-finish
The recommended minimum completionCriteria time is 60 seconds. To remove the
completion criteria, pass an empty string flag and manually mark the simulation
complete:
up alpha ctp simulate noop --changeset=./examples/noop/example-xr.yaml --complete-after=""
desiredState
The desiredState field specifies the current state of the simulation. The
simulation control plane status defaults to acceptingChanges until the
simulation meets the completionCriteria or you end the simulation.
To manually end a simulation, use kubectl to set the desiredState. A
simulation marked complete populates the result status and continues running.
A terminated simulation deletes the simulated control plane.
Use the simulations API
You can create a simulation using the API:
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: spaces.upbound.io/v1alpha1
kind: Simulation
metadata:
name: my-simulation
namespace: default
spec:
controlPlaneName: noop
desiredState: AcceptingChanges
completionCriteria:
- type: Duration
duration: 120s
EOF
Once you create the simulation object, Upbound populates the status field with
information about the simulation including:
- Created, modified, deleted resources
- The state of the simulation (Running, Completed, Terminated)
- Start and/or completion time
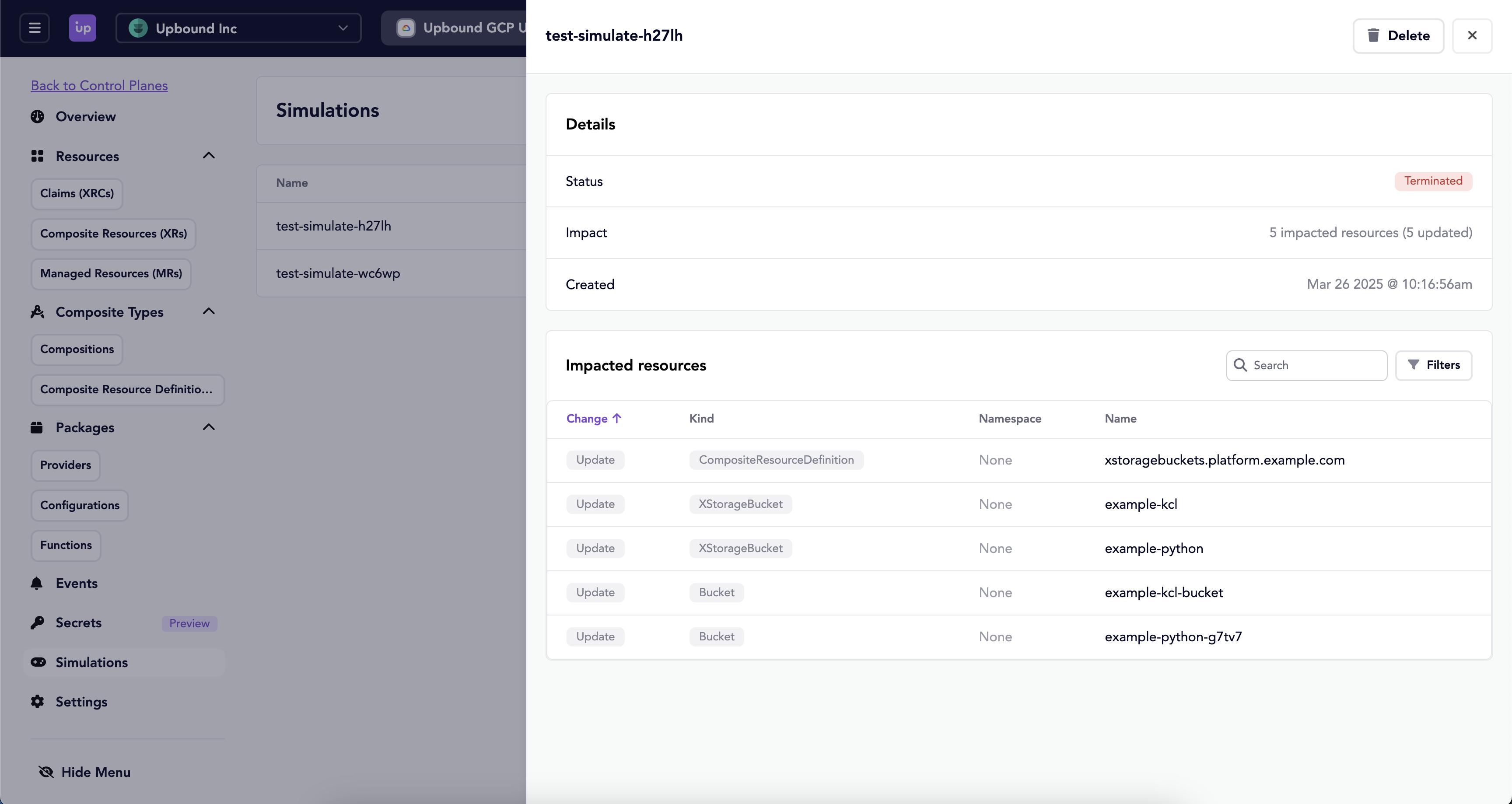
View simulation results in the Upbound Console
You can also view your simulation results in the Upbound Console:
- Navigate to your base control plane in the Upbound Console
- Select the "Simulations" tab in the menu
- Select a simulation object for a change list of all resources affected.
The Console provides visual indications of changes:
- Created Resources: Marked with green Modified Resources: Marked with yellow
- Deleted Resources: Marked with red Unchanged Resources: Displayed in gray
Managing your simulations
To view all simulations for a specific control plane, you can run the following command:
kubectl get simulations
The output returns all simulations associated with your control plane:
NAME SOURCE SIMULATED ACCEPTING-CHANGES STATE AGE
noop-6wqg9 noop noop-sim-1dcf6ed False SimulationTerminated 28m
To destroy your simulated control planes, you can manually delete them with
kubectl.
kubectl delete simulations <your_simulation_control_plane>
Considerations
Simulations is a private preview feature.
Be aware of the following limitations:
-
Simulations can't predict the exact behavior of external systems due to the complexity and non-deterministic reconciliation pattern in Crossplane.
-
The only completion criteria for a simulation is time. Your simulation may not receive a conclusive result within that interval. Upbound recommends the default
60svalue. -
Providers don't run in simulations. Simulations can't compose resources that rely on the status of Managed Resources.
The Upbound team is working to improve this feature. Your feedback is always appreciated.
Next steps
For general information on this feature as it fits in the Upbound workflow, review the overview documentation on Simulations.