API Connector
API Connector is currently in Preview. The feature is under active development and subject to breaking changes. Use for testing and evaluation purposes only.
API Connector enables seamless integration between Kubernetes application clusters consuming APIs and remote Crossplane control planes providing and reconciling APIs.
You can use the API Connector to decouple where Crossplane is running (for example in an Upbound control plane), and where APIs are consumed (for example in an existing Kubernetes cluster). This gives you flexibility and consistency in your control plane operations.
Unlike the Control Plane Connector which offers only coarse-grained connectivity between app clusters and a control plane, API connector offers fine-grained configuration of which APIs get offered along with multi-cluster connectivity.
Architecture overview
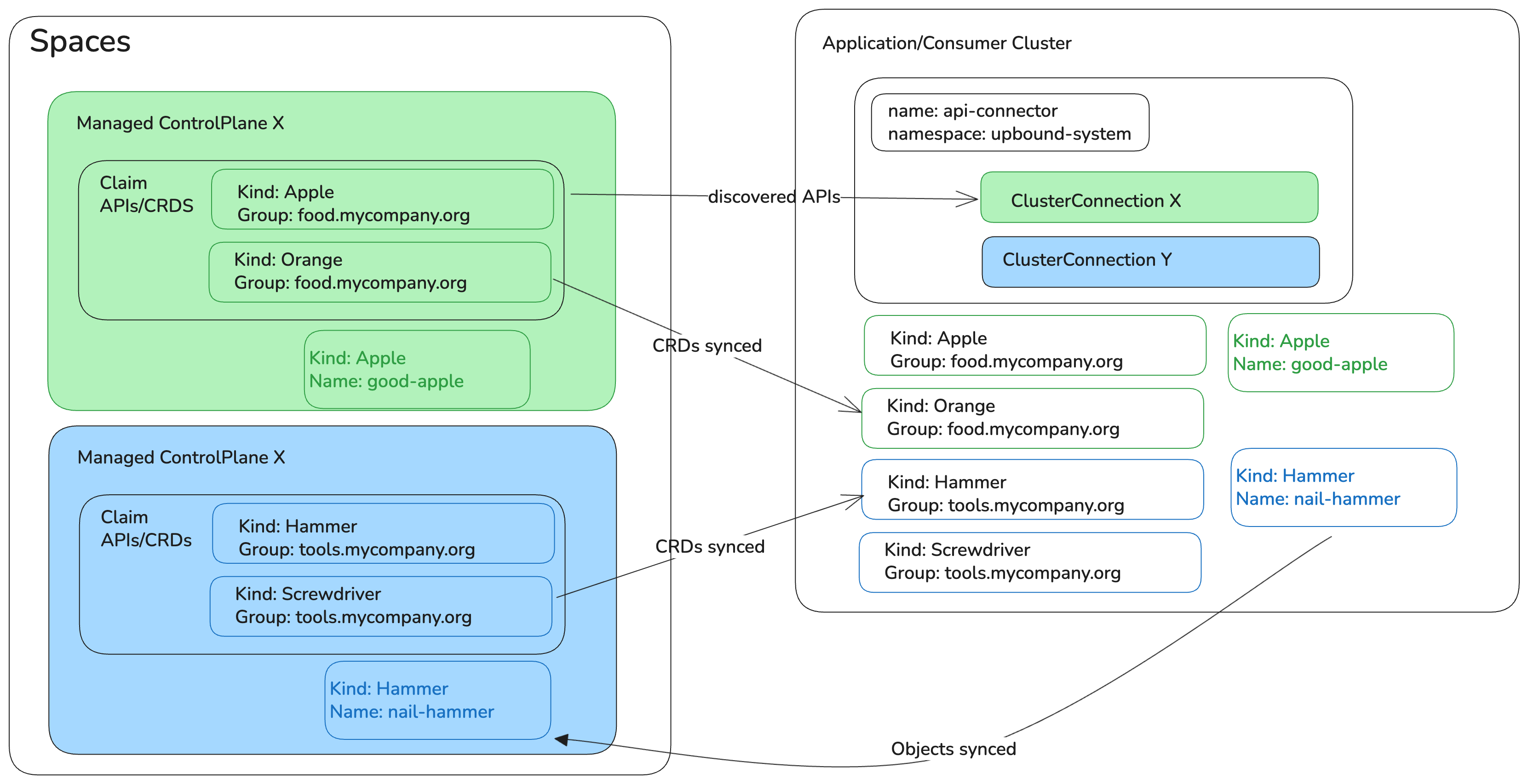
API Connector uses a provider-consumer model:
- Provider control plane: The Upbound control plane that provides APIs and manages infrastructure.
- Consumer cluster: Any Kubernetes cluster where its users wants to use APIs provided by the provider control plane, without having to run Crossplane. API connector gets installed in the consumer cluster, and bidirectionally syncs API objects to the provider.
Key components
Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs):
ClusterConnection: Establishes a connection from the consumer to the provider cluster. Pulls bindable CRD APIs from the provider into the consumer cluster for use.
ClusterAPIBinding: Instructs API connector to sync all API objects cluster-wide with a given API group to a given provider cluster.APIBinding: Namespaced version ofClusterAPIBinding. Instructs API connector to sync API objects within a given namespace and with a given API group to a given provider cluster.
Prerequisites
Before using API Connector, ensure:
- Consumer cluster has network access to the provider control plane
- You have an license to use API connector. If you are unsure, contact Upbound or your sales representative.
This guide walks through how to automate connecting your cluster to an Upbound control plane. You can also manually configure the API Connector.
Publishing APIs in the provider cluster
First, log in to your provider control plane, and choose which CRD APIs you want to make accessible to the consumer cluster's. API connector only syncs these "bindable" CRDs.
- Upbound Cloud
- Manual
Use the up CLI to login:
up login
Connect to your control plane:
up ctx <organization-name/space-name/group/provider-control-plane-name>
Check what CRDs are available:
kubectl get crds
Label all CRDs you want to publish with the bindable label:
kubectl label crd <crd-name> 'connect.upbound.io/bindable'='true' --overwrite
Change context to the provider cluster:
kubectl config set-context <provider-cluster-context>
Check what CRDs are available:
kubectl get crds
Label all CRDs you want to publish with the bindable label
kubectl label crd <CRD API name> 'connect.upbound.io/bindable'='true' --overwrite
Installation
- up CLI
- Manual
The up CLI provides the simplest installation method with automatic configuration:
Make sure the current Kubeconfig context is set to the provider control plane
up ctx <organization-name/space-name/group/provider-control-plane-name>
up controlplane api-connector install --consumer-kubeconfig <consumer-cluster-kubeconfig> [OPTIONS]
The command:
- creates a Robot account (named
<provider-control-plane-name>) in the Upbound Cloud organization<organization-name>, - Gives the created robot account
adminpermissions to the provider control plane<provider-control-plane-name> - Generates a JWT token for the robot account, and stores it in a Kubernetes Secret in the consumer cluster.
- Installs the API connector Helm chart in the consumer cluster.
- Creates a
ClusterConnectionobject in the consumer cluster, referring to the newly generated Secret, so that API connector can authenticate successfully to the provider control plane. - API connector pulls all published CRDs from the previous step into the consumer cluster.
Example:
up controlplane api-connector install \
--consumer-kubeconfig ~/.kube/config \
--consumer-context my-cluster \
--upbound-token <your-token>
This command uses provided token to authenticate with the Provider control plane
and create a ClusterConnection resource in the Consumer cluster to connect to the
Provider control plane.
Key Options:
--consumer-kubeconfig: Path to consumer cluster kubeconfig (required)--consumer-context: Context name for consumer cluster (required)--name: Custom name for connection resources (optional)--upbound-token: API token for authentication (optional)--upgrade: Upgrade existing installation (optional)--version: Specific version to install (optional)
For manual installation or custom configurations:
helm upgrade --install api-connector oci://xpkg.upbound.io/spaces-artifacts/api-connector \
--namespace upbound-system \
--create-namespace \
--version <version> \
--set consumerClusterDisplayName=<cluster-name>
Authentication methods
API Connector supports two authentication methods:
- Upbound Robot Token
- Kubeconfig
For Upbound Spaces integration:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: spaces-secret
namespace: upbound-system
type: Opaque
stringData:
token: <robot-token>
organization: <organization-name>
spacesBaseURL: <spaces-base-url>
controlPlaneGroupName: <control-plane-group-name>
controlPlaneName: <control-plane-name>
For direct cluster access:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: provider-kubeconfig
namespace: upbound-system
type: Opaque
data:
kubeconfig: <base64-encoded-kubeconfig>
Connection setup
Create a ClusterConnection to establish connectivity:
- Upbound Token
- Kubeconfig
apiVersion: connect.upbound.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterConnection
metadata:
name: spaces-connection
namespace: upbound-system
spec:
secretRef:
kind: UpboundRobotToken
name: spaces-secret
namespace: upbound-system
crdManagement:
pullBehavior: Pull
apiVersion: connect.upbound.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterConnection
metadata:
name: provider-connection
namespace: upbound-system
spec:
secretRef:
kind: KubeConfig
name: provider-kubeconfig
namespace: upbound-system
crdManagement:
pullBehavior: Pull
Configuration
Bind APIs to make them available in your consumer cluster:
apiVersion: connect.upbound.io/v1alpha1
kind: ClusterAPIBinding
metadata:
name: <crd-name>
spec:
connectionRef:
kind: ClusterConnection
name: <provider-controlplane-name> # Or --name value
The ClusterAPIBinding name must match the Resource.Group (name of the CustomResourceDefinition) of the CRD you want to bind.
Usage example
After configuration, you can create API objects (in the consumer cluster) that will be synchronized to the provider cluster:
apiVersion: nop.example.org/v1alpha1
kind: NopResource
metadata:
name: my-resource
namespace: default
spec:
coolField: "Synchronized resource"
compositeDeletePolicy: Foreground
Verify the resource status:
kubectl get nopresource my-resource -o yaml
When the APIBound=True condition is present, it means that the API object has
been synced to the provider cluster, and is being reconciled there. Whenever the
API object in the provider cluster gets status updates (for example
Ready=True), that status is synced back to the consumer cluster.
Switch contexts to the provider cluster to see the API object being created:
up ctx <organization-name/space-name/group/provider-control-plane-name>
# or kubectl config set-context <provider-cluster-context>
kubectl get nopresource my-resource -o yaml
Note that in the provider cluster, the API object is labeled with information on
where the API object originates from, and connect.upbound.io/managed=true.
Monitoring and troubleshooting
Check connection status
kubectl get clusterconnection
Expected output:
NAME STATUS MESSAGE
spaces-connection Ready Provider controlplane is available
View available APIs
kubectl get clusterconnection spaces-connection -o jsonpath='{.status.offeredAPIs[*].name}'
Check API binding status
kubectl get clusterapibinding
Debug resource synchronization
kubectl describe <resource-type> <resource-name>
Removal
Using the up CLI
up controlplane api-connector uninstall \
--consumer-kubeconfig ~/.kube/config \
--all
The --all flag removes all resources including connections and secrets.
Without the flag, only runtime related resources won't be removed.
Uninstall doesn't remove any API objects in the provider control plane. If you want to clean up all API objects there, delete all API objects from the consumer cluster before API connector uninstallation, and wait for the objects to get deleted.
Using Helm
helm uninstall api-connector -n upbound-system
Limitations
-
Preview feature: Subject to breaking changes. Not yet production grade.
-
CRD updates: CRDs are pulled once but not automatically updated. If multiple Crossplane clusters offer the same CRD API, API changes must be synchronized out of band, for example using a Crossplane Configuration.
-
Network requirements: Consumer cluster must have direct network access to provider cluster.
-
Wide permissions needed in consumer cluster: Because the API connector doesn't know up front the names of the APIs it needs to reconcile, it currently runs with full "root" privileges in the consumer cluster.
-
Connector polling: API Connector checks for drift between the consumer and provider cluster periodically through polling. The poll interval can be changed with the
pollIntervalHelm value.
Advanced configuration
Multiple connections
You can connect to multiple provider clusters simultaneously by creating multiple ClusterConnection resources with different names and configurations.