Authentication
The Upbound Official AWS Provider supports multiple authentication methods.
- Upbound auth (OIDC)
- AWS Access keys
- Assume role with web identity
- IAM roles for service accounts with AWS managed Kubernetes.
Upbound auth (OIDC)
This method of authentication is only supported in control planes running on Upbound Cloud Spaces
When your control plane runs in an Upbound Cloud Space, you can use this authentication method. Upbound authentication uses OpenID Connect (OIDC) to authenticate to AWS without requiring you to store credentials in Upbound.
Add Upbound as an OpenID Connect provider
- Open the AWS IAM console.
- Under the AWS IAM services, select Identity Providers > Add Provider.
- Select OpenID Connect and use https://proidc.upbound.io as the Provider URL and sts.amazonaws.com as the Audience. Select Get thumbprint. Select Add provider.
Create an AWS IAM Role for Upbound
- Create an AWS IAM Role with a Custom trust policy for the OIDC connector.
Provide your AWS account ID, Upbound organization and control plane names in the JSON Policy below.
You can find your AWS account ID by selecting the account dropdown in the upper right corner of the AWS console.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:oidc-provider/proidc.upbound.io"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"proidc.upbound.io:sub": "mcp:ORG_NAME/CONTROL_PLANE_NAME:provider:provider-aws",
"proidc.upbound.io:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
- Attach the permission policies you want for the control plane assuming this role.
- Name and create the role.
- View the new role and copy the role ARN.
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to Upbound.
Supply the role ARN created in the previous section.
To apply Upbound based authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Upbound
upbound:
webIdentity:
roleARN: <roleARN-for-provider-identity>
AWS authentication keys
Using AWS access keys, or long-term IAM credentials, requires storing the AWS keys as a Kubernetes secret.
To create the Kubernetes secret create or download your AWS access key ID and secret access key.
The format of the text file is
[default]
aws_access_key_id = AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
aws_secret_access_key = wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
Authentication keys with SSO
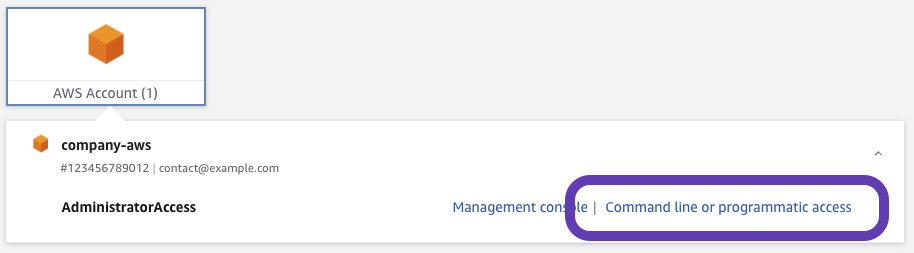
To generate authentication keys for SSO login, access your organization's AWS SSO portal.
Select "Command line or programmatic access"
Expand "Option 2" and copy the provided AWS credentials.
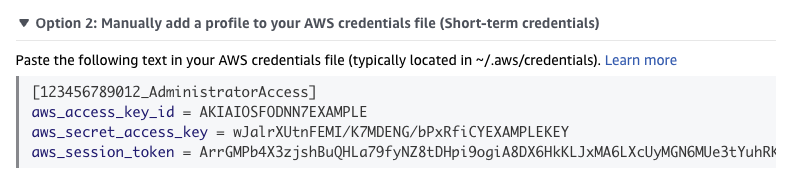
Use this as the contents of the aws-credentials.txt file.
Below is an example aws-credentials.txt file with SSO authentication.
[622346257358_AdministratorAccess]
aws_access_key_id=ASIAZBZV2IPHFUYQ2TFX
aws_secret_access_key=PPF/Wu9vTja98L5t/YNycbzEMw++aMt+jUZOpvtJ
aws_session_token=ArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zX
These credentials are only valid as long as your SSO session. When the credentials expire Crossplane can't monitor or change AWS resources.
Create a Kubernetes secret
Create the Kubernetes secret with kubectl create secret generic.
For example, name the secret aws-secret in the crossplane-system namespace and import the text file with the credentials aws-credentials.txt and assign them to the secret key my-aws-secret.
kubectl create secret generic \
aws-secret \
-n crossplane-system \
--from-file=my-aws-secret=./aws-credentials.txt
To create a secret declaratively requires encoding the authentication keys as a base-64 string.
Create a Secret object with the data containing the secret key name, my-aws-secret and the base-64 encoded keys.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-secret
namespace: crossplane-system
type: Opaque
data:
my-aws-secret: W2RlZmF1bHRdCmF3c19hY2Nlc3Nfa2V5X2lkID0gQUtJQUlPU0ZPRE5ON0VYQU1QTEUKYXdzX3NlY3JldF9hY2Nlc3Nfa2V5ID0gd0phbHJYVXRuRkVNSS9LN01ERU5HL2JQeFJmaUNZRVhBTVBMRUtFWQ==
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to Secret.
Create a secretRef with the namespace, name and key of the secret.
To apply key based authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-secret
key: my-aws-secret
To selectively apply key based authentication name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating an ProviderConfig named key-based-providerconfig.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: key-based-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-secret
key: my-aws-secret
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef.
apiVersion: s3.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-s3-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-2
providerConfigRef:
name: key-based-providerconfig
Role chaining
To use AWS IAM role chaining add a assumeRoleChain object to the ProviderConfig.
Inside the assumeRoleChain list one or more roles to assume, in order.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-secret
key: my-aws-secret
assumeRoleChain:
- roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
WebIdentity
When running the AWS Provider in an Amazon managed Kubernetes cluster (EKS)
the Provider may use
AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity
for authentication.
WebIdentity uses an OpenID Connect ID token to authenticate and use a specific AWS IAM role.
WebIdentity is only supported with Crossplane running in Amazon managed
Kubernetes clusters (EKS).
Configuring WebIdentity with the AWS Provider requires:
- an AWS IAM OIDC Provider
- an AWS IAM Role with an editable trust policy
- a ProviderConfig to enable WebIdentity authentication
Create an IAM OIDC provider
WebIdentity relies on the EKS cluster OIDC provider.
Follow the AWS instructions to create an IAM OIDC provider with your EKS OIDC provider URL.
Edit the IAM role
Supporting WebIdentity requires matching the EKS OIDC information to the specific role through a role trust policy.
Read the AWS trust policies blog for more information on trust policies.
The trust policy references the OIDC provider ARN and the provider AWS service account.
In the policy Principal enter "Federated": "<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>".
Add a Condition to restrict access to the role to only the Provider's service account.
The Condition uses StringLike to generically match the Provider's service account.
Why use a generic match?
The token used for authentication includes the full name of the AWS Provider's Kubernetes service account.
The Provider's service account name ends in a hash. If the hash changes the Condition doesn't match.
Enter the string (with quotation marks) ""<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>:sub": "system:serviceaccount:upbound-system:provider-aws-*".
Be sure to include :sub after the OIDC provider ARN.
The system:serviceaccount: matches the namespace where the Provider pod runs.
By default UXP uses upbound-system and Crossplane uses crossplane-system.
The following is a full example trust policy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5:sub": "system:serviceaccount:crossplane-system:provider-aws-*"
}
}
}
]
}
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to WebIdentity.
To apply WebIdentity authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
Apply the ARN of the role with the OIDC trust relationship as the roleARN field.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: WebIdentity
webIdentity:
roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
To selectively apply WebIdentity authentication name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating an ProviderConfig named webid-providerconfig.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: webid-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: WebIdentity
webIdentity:
roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef.
apiVersion: s3.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-s3-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-2
providerConfigRef:
name: webid-providerconfig
Role chaining
To use AWS IAM role chaining add a assumeRoleChain object to the ProviderConfig.
Inside the assumeRoleChain list one or more roles to assume, in order.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: webid-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: WebIdentity
webIdentity:
roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
assumeRoleChain:
- roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-assumed-role"
IAM roles for service accounts
When running the AWS Provider in an Amazon managed Kubernetes cluster (EKS)
the Provider may use
AWS IAM roles for service accounts
(IRSA) for authentication.
IRSA works by using an annotation on a Kubernetes ServiceAccount used by a Pod requesting AWS resources. The annotation matches an AWS IAM Role ARN configured with the desired permissions.
Configuring IRSA with the AWS Provider requires:
- an AWS IAM OIDC Provider
- an AWS IAM Role with an editable trust policy
- a DeploymentRuntimeConfig to add an annotation on the AWS Provider service account
- a ProviderConfig to enable IRSA authentication
Create an IAM OIDC provider
IRSA relies on the EKS cluster OIDC provider.
Follow the AWS instructions to create an IAM OIDC provider with your EKS OIDC provider URL.
Edit the IAM role
Supporting IRSA requires matching the EKS OIDC information to the specific role through a role trust policy.
Read the AWS trust policies blog for more information on trust policies.
The trust policy references the OIDC provider ARN and the provider AWS service account.
In the policy Principal enter "Federated": "<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>".
Add a Condition to restrict access to the role to only the Provider's service account.
The Condition uses StringLike to generically match the Provider's service account.
Why use a generic match?
The token used for authentication includes the full name of the AWS Provider's Kubernetes service account.
The Provider's service account name ends in a hash. If the hash changes the Condition doesn't match.
Enter the string (with quotation marks) ""<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>:sub": "system:serviceaccount:upbound-system:provider-aws-*".
Be sure to include :sub after the OIDC provider ARN.
The system:serviceaccount: matches the namespace where the Provider pod runs.
By default UXP uses upbound-system and Crossplane uses crossplane-system.
The following is a full example trust policy.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::622346257358:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5:sub": "system:serviceaccount:crossplane-system:provider-aws-*"
}
}
}
]
}
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig
IRSA relies on an annotation on the service account attached to a pod to identify the IAM role to use.
Crossplane uses a DeploymentRuntimeConfig to apply settings to the provider, including the provider service account.
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig object to apply a custom annotation to the provider service account.
In the metadata create an annotation with the key eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn and the value of the ARN of the AWS IAM role.
The spec is empty.
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: irsa-runtimeconfig
spec:
serviceAccountTemplate:
metadata:
annotations:
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::622346257358:role/my-custom-role
Apply the DeploymentRuntimeConfig
Install or update the provider with a runtimeConfigRef with the name of the DeploymentRuntimeConfig.
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-aws-s3
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-aws-s3:v0.37.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: irsa-runtimeconfig
After the provider finishes installing verify Crossplane applied the annotation on the service account from the DeploymentRuntimeConfig.
Kubernetes applies a unique hash to the end of the service account name.
Find the specific service account name with
kubectl get sa -n crossplane-system for Crossplane or
kubectl get sa -n upbound-system for UXP.
kubectl describe sa -n crossplane-system provider-aws-s3-dbc7f981d81f
Name: provider-aws-s3-dbc7f981d81f
Namespace: crossplane-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role
# Removed for brevity
Apply the runtimeConfig to each family provider using the same IAM role.
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to IRSA.
To apply IRSA authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: IRSA
To selectively apply IRSA authentication name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating an ProviderConfig named irsa-providerconfig.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: irsa-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: IRSA
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef.
apiVersion: s3.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-s3-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-2
providerConfigRef:
name: irsa-providerconfig
Role chaining
To use AWS IAM role chaining add a assumeRoleChain object to the ProviderConfig.
Inside the assumeRoleChain list one or more roles to assume, in order.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: irsa-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: IRSA
assumeRoleChain:
- roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-assumed-role"