Provider Authentication
This guide covers authentication methods for Upbound Official Providers. Each provider supports multiple authentication approaches to fit different deployment scenarios and security requirements.
Quick reference
| Provider | Authentication Methods |
|---|---|
| AWS | Upbound OIDC, Access Keys, WebIdentity, IRSA |
| Azure | Upbound OIDC, Service Principal, Managed Identity |
| GCP | Upbound OIDC, Service Account Keys, OAuth 2.0 Token, Service Account Impersonation, Workload Identity |
| Kubernetes | Upbound Identity, Injected Identity, Injected Identity with Cloud Provider Credentials |
| Helm | Injected Identity with Cloud Provider Credentials |
AWS authentication
The Upbound Official AWS Provider supports multiple authentication methods suitable for different environments.
AWS Upbound OIDC
This method is only supported in control planes running on Upbound Cloud Spaces.
Upbound authentication uses OpenID Connect (OIDC) to authenticate to AWS without storing credentials in Upbound.
Add Upbound as an OpenID Connect provider
- Open the AWS IAM console.
- Under AWS IAM services, select Identity Providers > Add Provider.
- Select OpenID Connect and use https://proidc.upbound.io as the Provider URL and sts.amazonaws.com as the Audience.
- Select Get thumbprint.
- Select Add provider.
Create an AWS IAM Role for Upbound
- Create an AWS IAM Role with a Custom trust policy for the OIDC connector.
Provide your AWS account ID, Upbound organization and control plane names in the JSON Policy below.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::YOUR_AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:oidc-provider/proidc.upbound.io"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"proidc.upbound.io:sub": "mcp:ORG_NAME/CONTROL_PLANE_NAME:provider:provider-aws",
"proidc.upbound.io:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
- Attach the permission policies you want for the control plane assuming this role.
- Name and create the role.
- View the new role and copy the role ARN.
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to Upbound.
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Upbound
upbound:
webIdentity:
roleARN: <roleARN-for-provider-identity>
AWS Access Keys
Using AWS access keys requires storing the AWS keys as a Kubernetes secret.
Create or download your AWS access key ID and secret access key. The format of the text file is:
[default]
aws_access_key_id = AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
aws_secret_access_key = wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
Authentication keys with SSO
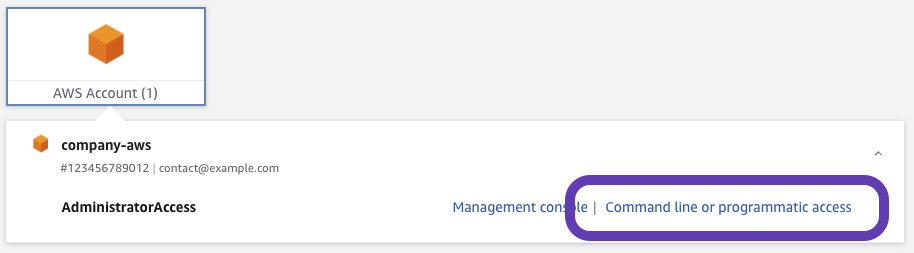
To generate authentication keys for SSO login, access your organization's AWS SSO portal.
Select "Command line or programmatic access"
Expand "Option 2" and copy the provided AWS credentials.
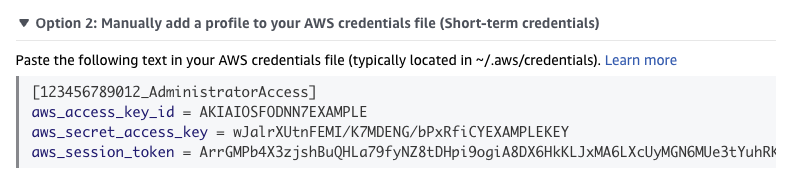
Use this as the contents of the aws-credentials.txt file.
Below is an example aws-credentials.txt file with SSO authentication.
[123456789_AdministratorAccess]
aws_access_key_id=ASIAZBZV2IPKEXAMPLEKEY
aws_secret_access_key=PPF/Wu9vTja98L5t/YNycbzEMEXAMPLEKEY
aws_session_token=ArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zXArrGMPb4X3zjshBuQHLa79fyNZ8tDHpi9ogiA8DX6HkKLJxMA6LXcUyMGN6MUe3tYuhRKwdCTkfwt6qCVMT8Ctab//3jMmrV9zX
These credentials are only valid as long as your SSO session. When the credentials expire Crossplane can't monitor or change AWS resources.
Create a Kubernetes secret
Create the Kubernetes secret with kubectl create secret generic:
kubectl create secret generic \
aws-secret \
-n crossplane-system \
--from-file=my-aws-secret=./aws-credentials.txt
To create a secret declaratively requires encoding the authentication keys as a base-64 string.
Create a Secret object with the data containing the secret key name and the base-64 encoded keys:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: aws-secret
namespace: crossplane-system
type: Opaque
data:
my-aws-secret: W2RlZmF1bHRdCmF3c19hY2Nlc3Nfa2V5X2lkID0gQUtJQUlPU0ZPRE5ON0VYQU1QTEUKYXdzX3NlY3JldF9hY2Nlc3Nfa2V5ID0gd0phbHJYVXRuRkVNSS9LN01ERU5HL2JQeFJmaUNZRVhBTVBMRUtFWQ==
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to Secret:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-secret
key: my-aws-secret
To apply key based authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
To selectively apply key based authentication, name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating a ProviderConfig named key-based-providerconfig:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: key-based-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-secret
key: my-aws-secret
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef:
apiVersion: s3.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-s3-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-2
providerConfigRef:
name: key-based-providerconfig
Role chaining
To use AWS IAM role chaining, add an assumeRoleChain object to the ProviderConfig.
Inside the assumeRoleChain, list one or more roles to assume, in order:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: aws-secret
key: my-aws-secret
assumeRoleChain:
- roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
AWS WebIdentity
When running in an Amazon managed Kubernetes cluster (EKS), the Provider may use AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity for authentication.
WebIdentity uses an OpenID Connect ID token to authenticate and use a specific AWS IAM role.
WebIdentity is only supported with Crossplane running in Amazon managed Kubernetes clusters (EKS).
Configuring WebIdentity with the AWS Provider requires:
- An AWS IAM OIDC Provider
- An AWS IAM Role with an editable trust policy
- A ProviderConfig to enable WebIdentity authentication
Create an IAM OIDC provider
WebIdentity relies on the EKS cluster OIDC provider.
Follow the AWS instructions to create an IAM OIDC provider with your EKS OIDC provider URL.
Edit the IAM role
Supporting WebIdentity requires matching the EKS OIDC information to the specific role through a role trust policy.
Read the AWS trust policies blog for more information on trust policies.
The trust policy references the OIDC provider ARN and the provider AWS service account.
In the policy Principal enter "Federated": "<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>".
Add a Condition to restrict access to the role to only the Provider's service account.
The Condition uses StringLike to generically match the Provider's service account.
Why use a generic match?
The token used for authentication includes the full name of the AWS Provider's Kubernetes service account.
The Provider's service account name ends in a hash. If the hash changes the Condition doesn't match.
Enter the string (with quotation marks) "<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>:sub": "system:serviceaccount:upbound-system:provider-aws-*".
Be sure to include :sub after the OIDC provider ARN.
The system:serviceaccount: matches the namespace where the Provider pod runs.
By default UXP uses upbound-system and Crossplane uses crossplane-system.
The following is a full example trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5:sub": "system:serviceaccount:crossplane-system:provider-aws-*"
}
}
}
]
}
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to WebIdentity:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: WebIdentity
webIdentity:
roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
To apply WebIdentity authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
To selectively apply WebIdentity authentication, name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating a ProviderConfig named webid-providerconfig:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: webid-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: WebIdentity
webIdentity:
roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef:
apiVersion: s3.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-s3-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-2
providerConfigRef:
name: webid-providerconfig
Role chaining
To use AWS IAM role chaining, add an assumeRoleChain object to the ProviderConfig.
Inside the assumeRoleChain, list one or more roles to assume, in order:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: webid-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: WebIdentity
webIdentity:
roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role"
assumeRoleChain:
- roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-assumed-role"
AWS IRSA
When running in Amazon EKS, the Provider may use IAM roles for service accounts (IRSA) for authentication.
IRSA works by using an annotation on a Kubernetes ServiceAccount used by a Pod requesting AWS resources. The annotation matches an AWS IAM Role ARN configured with the desired permissions.
Configuring IRSA with the AWS Provider requires:
- An AWS IAM OIDC Provider
- An AWS IAM Role with an editable trust policy
- A DeploymentRuntimeConfig to add an annotation on the AWS Provider service account
- A ProviderConfig to enable IRSA authentication
Create an IAM OIDC provider
IRSA relies on the EKS cluster OIDC provider.
Follow the AWS instructions to create an IAM OIDC provider with your EKS OIDC provider URL.
Edit the IAM role
Supporting IRSA requires matching the EKS OIDC information to the specific role through a role trust policy.
Read the AWS trust policies blog for more information on trust policies.
The trust policy references the OIDC provider ARN and the provider AWS service account.
In the policy Principal enter "Federated": "<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>".
Add a Condition to restrict access to the role to only the Provider's service account.
The Condition uses StringLike to generically match the Provider's service account.
Why use a generic match?
The token used for authentication includes the full name of the AWS Provider's Kubernetes service account.
The Provider's service account name ends in a hash. If the hash changes the Condition doesn't match.
Enter the string (with quotation marks) "<OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN>:sub": "system:serviceaccount:upbound-system:provider-aws-*".
Be sure to include :sub after the OIDC provider ARN.
The system:serviceaccount: matches the namespace where the Provider pod runs.
By default UXP uses upbound-system and Crossplane uses crossplane-system.
The following is a full example trust policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::622346257358:oidc-provider/oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"oidc.eks.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/id/5C64F628ACFB6A892CC25AF3B67124C5:sub": "system:serviceaccount:crossplane-system:provider-aws-*"
}
}
}
]
}
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig
IRSA relies on an annotation on the service account attached to a pod to identify the IAM role to use.
Crossplane uses a DeploymentRuntimeConfig to apply settings to the provider, including the provider service account.
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig object to apply a custom annotation to the provider service account:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: irsa-runtimeconfig
spec:
serviceAccountTemplate:
metadata:
annotations:
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::622346257358:role/my-custom-role
Apply the DeploymentRuntimeConfig
Install or update the provider with a runtimeConfigRef:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-aws-s3
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-aws-s3:v2.1.1
runtimeConfigRef:
name: irsa-runtimeconfig
After the provider finishes installing, verify Crossplane applied the annotation on the service account from the DeploymentRuntimeConfig.
Kubernetes applies a unique hash to the end of the service account name. Find the specific service account name with kubectl get sa -n crossplane-system for Crossplane or kubectl get sa -n upbound-system for UXP.
kubectl describe sa -n crossplane-system provider-aws-s3-dbc7f981d81f
Name: provider-aws-s3-dbc7f981d81f
Namespace: crossplane-system
Labels: <none>
Annotations: eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn: arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-custom-role
# Removed for brevity
Apply the runtimeConfig to each family provider using the same IAM role.
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to IRSA:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: IRSA
To apply IRSA authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
To selectively apply IRSA authentication, name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating a ProviderConfig named irsa-providerconfig:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: irsa-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: IRSA
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef:
apiVersion: s3.aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-s3-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-2
providerConfigRef:
name: irsa-providerconfig
Role chaining
To use AWS IAM role chaining, add an assumeRoleChain object to the ProviderConfig.
Inside the assumeRoleChain, list one or more roles to assume, in order:
apiVersion: aws.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: irsa-providerconfig
spec:
credentials:
source: IRSA
assumeRoleChain:
- roleARN: "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/my-assumed-role"
Azure authentication
The Upbound Official Azure Provider supports multiple authentication methods.
Azure Upbound OIDC
This method is only supported in control planes running on Upbound Cloud Spaces.
Create an identity pool
- Open the Azure portal.
- Select Microsoft Entra ID.
- Select App registrations.
- Select New registration.
- Name the pool upbound-oidc-provider.
- In Supported account types select Accounts in this organizational directory only.
- Leave Redirect URI blank.
- Select Register.
Create a federated credential
- Select Certificates and secrets in the left navigation.
- Select Federated credentials tab.
- Select Add credential.
- In Federated credential scenario select Other Issuer.
- In Issuer enter https://proidc.upbound.io.
- In Subject identifier enter:
mcp:<your-org>/<your-control-plane-name>:provider:provider-azure - In Audience leave api://AzureADTokenExchange.
- In Name enter a name for the credential, like:
upbound-<your-org>-<your-control-plane-name>-provider-azure - In Description optionally enter a description, like:
Upbound MCP <your-org>/<your-control-plane-name> Provider provider-azure - Select Add.
Grant permissions to the service principal
For your control plane to be able to perform actions required by this configuration, you need to grant permissions to the Application Service Principal. Assign a role to the Application Service Principal by following these instructions:
- Open the Azure portal
- Select Subscriptions.
- Select your subscription.
- Select Access control (IAM) in the left navigation.
- Select Add and select Add role assignment.
- Find and select the Contributor role on the Privileged administrator roles tab.
- Select Next.
- In Assign access to select User, group, or service principal.
- Select Select members.
- Find your application by entering upbound-oidc-provider in the search field.
- Select Select.
- Select Review + assign.
- Make sure everything is correct and press Review + assign again.
Create a ProviderConfig
apiVersion: azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Upbound
clientID: <client ID>
tenantID: <tenant ID>
subscriptionID: <subscription ID>
Azure Service Principal
A service principal passes client_id, client_secret, and tenant_id authentication tokens to create and manage Azure resources.
Create a service principal using Azure CLI
Find your Subscription ID:
az account list
Create a service principal with Owner role:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --sdk-auth --role Owner --scopes /subscriptions/<subscription_id> \
> azure.json
Create a Kubernetes secret
kubectl create secret generic azure-secret -n upbound-system --from-file=creds=./azure.json
The azure.json file contains the client ID, secret, and tenant ID of your subscription.
Create a ProviderConfig
apiVersion: azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: default
kind: ProviderConfig
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: upbound-system
name: azure-secret
key: creds
Your credential source must be Secret and you must specify the namespace, name, and key if you used different values.
Service principal with client certificate credentials
You can create Azure service principals with a client certificate instead of a client secret as credentials. When creating the service principal, Azure CLI provides the options to generate a client certificate automatically or set your own custom certificate.
Create a service principal with a generated client certificate
The following command creates a service principal with an automatically generated certificate:
# set your subscription ID
AZ_SUBSCRIPTION_ID="11111111-1111-1111-1111-1111111111111"
az ad sp create-for-rbac --sdk-auth \
--role Owner \
--scopes /subscriptions/"${AZ_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}" \
--create-cert > azure_credentials.json
The azure_credentials.json file contains:
- The client ID
- The path of the generated client certificate file in your local machine
- Tenant ID of your subscription
It looks like the following:
{
"clientId": "1111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555",
"clientCertificate": "/path/to/generatedcert.pem",
"subscriptionId": "22222222-3333-4444-5555-666666666666",
"tenantId": "33333333-4444-5555-6666-777777777777",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"activeDirectoryGraphResourceId": "https://graph.windows.net/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}
The generated certificate looks like the following:
-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----
...
-----END PRIVATE KEY-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
To use this configuration with the Upbound Azure Provider, you should replace the clientCertificate field with the certificate content. First convert the certificate to PKCS12 format, then encode it with base64:
# extract the path of the generated PEM certificate
AZ_CLIENT_CERT_PEM_PATH="$(jq -r '.clientCertificate' azure_credentials.json)"
# convert PEM to PKCS12 using openssl tool
openssl pkcs12 -export \
-out azure_sp_cert.pkcs12 \
-in "${AZ_CLIENT_CERT_PEM_PATH}" \
-inkey "${AZ_CLIENT_CERT_PEM_PATH}" \
-passout pass:
# encode the certificate
base64 -i azure_sp_cert.pkcs12 | tr -d '\n' > azure_sp_cert_pkcs12_base64encoded
# replace clientCertificate field in azure_credentials.json with base64-encoded certificate content
jq --rawfile certcontent azure_sp_cert_pkcs12_base64encoded \
'.clientCertificate=$certcontent' azure_credentials.json > azure_credentials_withcert.json
The preceding command snippet should generate the file azure_credentials_withcert.json that looks like the following:
{
"clientId": "1111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555",
"clientCertificate": "XXXXX......XXX",
"subscriptionId": "22222222-3333-4444-5555-666666666666",
"tenantId": "33333333-4444-5555-6666-777777777777",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"activeDirectoryGraphResourceId": "https://graph.windows.net/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}
Next, use kubectl to associate your Azure credentials file with a generic Kubernetes secret:
kubectl create secret generic azure-secret -n upbound-system --from-file=creds=./azure_credentials_withcert.json
Create a service principal with your own client certificate
Azure service principals accept custom certificates in an ASCII format such as PEM, CER, or DER. When using a certificate with PEM format, the certificate file should include both the certificate and private key appended. See Microsoft Azure Service Principal Documentation for reference.
The following command creates a service principal with your custom certificate. You can choose one of the options:
# option 1 - load cert from file
az ad sp create-for-rbac --sdk-auth \
--role Owner \
--scopes /subscriptions/"${AZ_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}" \
--cert @/path/to/yourcert.pem > azure_credentials.json
# option 2 - set cert directly from string
az ad sp create-for-rbac --sdk-auth \
--role Owner \
--scopes /subscriptions/"${AZ_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}" \
--cert "-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n...-----END CERTIFICATE-----" > azure_credentials.json
The preceding command generates the azure_credentials.json file. Since you used a custom certificate, note that clientCertificate is null in the output:
{
"clientId": "1111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555",
"clientCertificate": null,
"subscriptionId": "22222222-3333-4444-5555-666666666666",
"tenantID": "33333333-4444-5555-6666-777777777777",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"activeDirectoryGraphResourceId": "https://graph.windows.net/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}
Upbound Azure Provider accepts certificates in base64-encoded PKCS12 format. Convert your certificate to PKCS12 format, then encode it with base64. Add the resulting string to the clientCertificate field of azure_credentials.json.
In the snippet below, you can find example commands for PEM certificate to PKCS12 conversion using openssl. If your certificate is in other formats than PEM, you can convert it to PEM, then use the following commands for PKCS12 conversion. If you already have your certificate in PKCS12 format, you can skip the conversion and move to the base64 encode step:
# convert PEM to PKCS12 using openssl tool
openssl pkcs12 -export \
-out azure_sp_cert.pkcs12 \
-in "/path/to/your/cert.pem" \
-inkey "/path/to/your/key.pem" \
-passout pass:
# encode
base64 -i azure_sp_cert.pkcs12 | tr -d '\n' > azure_sp_cert_pkcs12_base64encoded
# replace clientCertificate field in azure_credentials.json with base64-encoded certificate content
jq --rawfile certcontent azure_sp_cert_pkcs12_base64encoded \
'.clientCertificate=$certcontent' azure_credentials.json > azure_credentials_withcert.json
If you have a password-protected PKCS12 certificate, you should also set the clientCertificatePassword field in the azure_credentials_withcert.json:
{
"clientId": "1111111-2222-3333-4444-555555555555",
"clientCertificate": "XXXXX......XXX",
"clientCertificatePassword": "YourClientCertificatePassword",
"subscriptionId": "22222222-3333-4444-5555-666666666666",
"tenantId": "33333333-4444-5555-6666-777777777777",
"activeDirectoryEndpointUrl": "https://login.microsoftonline.com",
"resourceManagerEndpointUrl": "https://management.azure.com/",
"activeDirectoryGraphResourceId": "https://graph.windows.net/",
"sqlManagementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net:8443/",
"galleryEndpointUrl": "https://gallery.azure.com/",
"managementEndpointUrl": "https://management.core.windows.net/"
}
Use kubectl to associate your Azure credentials file with a generic Kubernetes secret:
kubectl create secret generic azure-secret -n upbound-system --from-file=creds=./azure_credentials_withcert.json
Azure Managed Identity
The system-assigned managed identity allows you to associate the provider with your Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster automatically without manually managing credentials.
System-assigned managed identity
A system-assigned managed identity is automatically created when you create an AKS cluster. This section covers creating a new identity in a new cluster.
Create a resource group:
az group create --name myResourceGroup --location westus2
Create an AKS cluster with the --enable-managed-identity flag:
az aks create -g myResourceGroup -n myManagedCluster --enable-managed-identity
Use the aks get-credentials command to generate the kubeconfig file for your AKS cluster. This file contains the authentication and connection information for your cluster:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myManagedCluster
To switch from a service principal to a system-assigned managed identity, use the aks update command:
az aks update -g myResourceGroup -n myManagedCluster --enable-managed-identity
Configure your provider
In your provider configuration, update the source, subscriptionID, and tenantID in the credentials field:
apiVersion: azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: SystemAssignedManagedIdentity
subscriptionID: <subscription_ID>
tenantID: <tenant_ID>
User-assigned managed identity
Create user-assigned managed identities:
az identity create --name <controlplane_identity_name> --resource-group <resource_group>
az identity create --name <kubelet_identity_name> --resource-group <resource_group>
Create an AKS cluster with the identities:
az aks create \
--resource-group <resource_group> \
--name <cluster_name> \
--enable-managed-identity \
--assign-identity <controlplane_identity_resource_id> \
--assign-kubelet-identity <kubelet_identity_resource_id>
Create a ProviderConfig:
apiVersion: azure.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: UserAssignedManagedIdentity
clientID: <kubelet_identity_id>
subscriptionID: <subscription_ID>
tenantID: <tenant_ID>
GCP authentication
The Upbound Official GCP Provider supports multiple authentication methods.
GCP Upbound OIDC
This method is only supported in control planes running on Upbound Cloud Spaces.
Create an identity pool
- Open the GCP IAM Admin console.
- Select Workload Identity Federation.
- Select Create Pool.
- Name the pool upbound-oidc-pool.
- Enable the pool.
- Select Continue.
Add Upbound to the pool
- Provider Name: upbound-oidc-provider
- Issuer (URL): https://proidc.upbound.io
- Audience 1: sts.googleapis.com
The provider attributes restrict which remote entities you allow access to your resources. When Upbound authenticates to GCP it provides an OIDC subject (sub) in the form:
mcp:<account>/<mcp-name>:provider:<provider-name>
Configure the google.subject attribute as assertion.sub.
Under Attribute Conditions select Add Condition.
To authenticate any control plane in your organization, in the Conditional CEL input box enter:
google.subject.contains("mcp:ORGANIZATION_NAME")
Not providing a CEL condition allows any control plane to access your GCP account if they know the project ID and service account name.
Select Save.
Create a GCP Service Account
- Open the GCP IAM Admin console.
- Select Service Accounts.
- Select Create Service Account.
- Grant appropriate roles (for example, Cloud SQL Admin, Workload Identity User).
Add the service account to the identity pool
- Return to Workload Identity Federation.
- Select Grant Access.
- Select your service account.
- Use All identities in the pool.
Create a ProviderConfig
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
projectID: <project-id>
credentials:
source: Upbound
upbound:
federation:
providerID: projects/<project-id>/locations/global/workloadIdentityPools/<identity-pool>/providers/<identity-provider>
serviceAccount: <service-account-name>@<project-name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com
GCP Service Account Keys
Using GCP service account keys requires storing the GCP account keys JSON file as a Kubernetes secret.
To create the Kubernetes secret, create or download your GCP service account key JSON file.
Create a Kubernetes secret
Create the Kubernetes secret with kubectl create secret generic:
kubectl create secret generic \
gcp-secret \
-n crossplane-system \
--from-file=my-gcp-secret=./gcp-credentials.json
To create a secret declaratively requires encoding the authentication keys as a base-64 string.
Create a Secret object with the data containing the secret key name and the base-64 encoded keys:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: gcp-secret
namespace: crossplane-system
type: Opaque
data:
my-gcp-secret: ewogICJ0eXBlIjogInNlcnZpY2VfYWNjb3VudCIsCiAgInByb2plY3RfaWQiOiAiZG9jcyIsCiAgInByaXZhdGVfa2V5X2lkIjogIjEyMzRhYmNkIiwKICAicHJpdmF0ZV9rZXkiOiAiLS0tLS1CRUdJTiBQUklWQVRFIEtFWS0tLS0tXG5cbi0tLS0tRU5EIFBSSVZBVEUgS0VZLS0tLS1cbiIsCiAgImNsaWVudF9lbWFpbCI6ICJkb2NzQHVwYm91bmQuaWFtLmdzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC5jb20iLAogICJjbGllbnRfaWQiOiAiMTIzNDUiLAogICJhdXRoX3VyaSI6ICJodHRwczovL2FjY291bnRzLmdvb2dsZS5jb20vby9vYXV0aDIvYXV0aCIsCiAgInRva2VuX3VyaSI6ICJodHRwczovL29hdXRoMi5nb29nbGVhcGlzLmNvbS90b2tlbiIsCiAgImF1dGhfcHJvdmlkZXJfeDUwOV9jZXJ0X3VybCI6ICJodHRwczovL3d3dy5nb29nbGVhcGlzLmNvbS9vYXV0aDIvdjEvY2VydHMiLAogICJjbGllbnRfeDUwOV9jZXJ0X3VybCI6ICJodHRwczovL3d3dy5nb29nbGVhcGlzLmNvbS9yb2JvdC92MS9tZXRhZGF0YS94NTA5L2RvY3MuaWFtLmdzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudC5jb20iLAogICJ1bml2ZXJzZV9kb21haW4iOiAiZ29vZ2xlYXBpcy5jb20iCn0=
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to Secret:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
projectID: <project-id>
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: gcp-secret
key: my-gcp-secret
To apply key based authentication by default name the ProviderConfig default.
To selectively apply key based authentication, name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating a ProviderConfig named key-based-providerconfig:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: key-based-providerconfig
spec:
projectID: <project-id>
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: gcp-secret
key: my-gcp-secret
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef:
apiVersion: storage.gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-gcp-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
location: US
providerConfigRef:
name: key-based-providerconfig
GCP OAuth 2.0 Access Token
Using GCP access tokens requires storing the GCP account keys JSON file as a Kubernetes secret.
Create a GCP access token for a service account or with the gcloud CLI.
GCP access tokens are valid for 1 hour by default. When the token expires Crossplane can't create or delete resources.
The provider-gcp GitHub repository contains an example cron job that automatically refreshes access tokens.
Create a Kubernetes secret
Create the Kubernetes secret with kubectl create secret generic:
kubectl create secret generic \
gcp-secret \
-n crossplane-system \
--from-file=my-gcp-secret=./gcp-token.json
To create a secret declaratively requires encoding the access token as a base-64 string.
Create a Secret object with the data containing the secret key name and the base-64 encoded token:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: gcp-secret
namespace: crossplane-system
type: Opaque
data:
my-gcp-secret: eWEyOS5hMEFmQl9ieURVVEpSSWt3RDk1c1cxTGE0d3dlLS0xTHpOZkxJeFFYbnIza25VVG9jYV9xY2xsSG1ZUzVycjJwYmNzZnVuR3M5blR6SnVIb2lYb3VmRnBEbGZicGV5bTBJU1lfUmdxWGNCMTdDY3RXZWZOd2hJcVVUblJ2UVdmcHpsODVvbklzUXZaN0F5MEJjUy1ZMGxXYXJXODVJQ2Z5R0RhZEtvYUNnWUtBWXdTQVJFU0ZRSHN2WWxzUnU1Q0w4UVY0OThRc1pvbmxGVXJXQTAxNzE=
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to AccessToken:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
projectID: <project-id>
credentials:
source: AccessToken
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: gcp-secret
key: my-gcp-secret
To selectively apply token based authentication, name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating a ProviderConfig named token-based-providerconfig:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: token-based-providerconfig
spec:
projectID: <project-id>
credentials:
source: AccessToken
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: gcp-secret
key: my-gcp-secret
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef:
apiVersion: storage.gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-gcp-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
location: US
providerConfigRef:
name: token-based-providerconfig
GCP Service Account Impersonation
When running the GCP Provider in Google managed Kubernetes cluster (GKE), the Provider may use service account impersonation for authentication.
Account impersonation allows the Provider to authenticate to GCP APIs using one service account and request escalated privileges through a second account.
Service account impersonation is only supported with Crossplane running in Google managed Kubernetes clusters (GKE).
Configuring service account impersonation with the GCP Provider requires:
- A lower privileged GCP service account
- An elevated privileged GCP service account
- A DeploymentRuntimeConfig to reference the lower-privileged GCP service account
- A ProviderConfig to reference the elevated privileged GCP service account
Configure the GCP service accounts
You may use existing service accounts or follow the GCP documentation to create new service accounts.
The lower privilege role requires a GCP IAM policy binding role for the project which includes iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding <Project_Name> \
--member "serviceAccount:<Lower_Privilege_Service_Account>@<Project_Name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator \
--project <Project_Name>
For example, to create a role-binding for project upbound and account docs-unprivileged:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding upbound \
--member "serviceAccount:docs-unprivileged@upbound.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role roles/iam.serviceAccountTokenCreator \
--project upbound
The lower privileged service account requires a GCP IAM service account policy binding between the unprivileged account and the Kubernetes provider service account:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding <Lower_Privilege_Service_Account>@<Project_Name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:<Project_Name>.svc.id.goog[<Crossplane_Namespace>/<Kubernetes_Service_Account_Name>]"
For example, to create a policy binding for project upbound, account docs-unprivileged, namespace crossplane-system, and Provider service account name gcp-provider-sa:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding docs-unprivileged@upbound.iam.gserviceaccount.com \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:upbound.svc.id.goog[crossplane-system/gcp-provider-sa]"
For more information on the account requirements for account impersonation, read the GCP service account impersonation documentation.
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig
The DeploymentRuntimeConfig creates a custom Provider service account and applies an annotation to the Provider's pod.
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig object. Add an annotation mapping the key iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account to the email address of the lower-privileged GCP IAM service account.
Add a serviceAccountName to the spec to create the Provider's service account. This must match the name used in the GCP IAM binding:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: impersonation-runtimeconfig
spec:
serviceAccountTemplate:
metadata:
annotations:
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account: <Lower_Privilege_Service_Account>@<Project_Name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com
name: <Kubernetes_service_account_name>
For example, to use a GCP service account named docs-unprivileged and a service account name gcp-provider-sa:
The serviceAccountName must match the service account referenced in the GCP IAM policy binding.
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: impersonation-runtimeconfig
spec:
serviceAccountTemplate:
metadata:
annotations:
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account: docs-unprivileged@upbound.iam.gserviceaccount.com
name: gcp-provider-sa
Apply the DeploymentRuntimeConfig
Install or update the provider with a runtimeConfigRef:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-gcp-storage
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-gcp-storage:v2.1.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: impersonation-runtimeconfig
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig to set the provider authentication method to ImpersonateServiceAccount. Add the impersonateServiceAccount object and provide the name of the privileged account to impersonate. Include the projectID to use:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
projectID: <Project_Name>
credentials:
source: ImpersonateServiceAccount
impersonateServiceAccount:
name: <Privileged_Service_Account>@<Project_Name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com
For example, to create a ProviderConfig with service account named docs-privileged and project named upbound:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
projectID: upbound
credentials:
source: ImpersonateServiceAccount
impersonateServiceAccount:
name: docs-privileged@upbound.iam.gserviceaccount.com
To selectively apply impersonation based authentication, name the ProviderConfig and apply it when creating managed resources.
For example, creating a ProviderConfig named impersonation-providerconfig:
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: impersonation-providerconfig
spec:
projectID: <Project_Name>
credentials:
source: ImpersonateServiceAccount
impersonateServiceAccount:
name: <Privileged_Service_Account>@<Project_Name>.iam.gserviceaccount.com
Apply the ProviderConfig to a managed resource with a providerConfigRef:
apiVersion: storage.gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: Bucket
metadata:
name: my-gcp-bucket
spec:
forProvider:
location: US
providerConfigRef:
name: impersonation-providerconfig
GCP Workload Identity
When running in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), the Provider may use workload identity for authentication.
Workload identity is only supported with Crossplane running in GKE.
Configure the GCP service account
Enable workload identity and link the GCP IAM service account:
gcloud iam service-accounts add-iam-policy-binding \
<Service_Account_Email_Address> \
--role roles/iam.workloadIdentityUser \
--member "serviceAccount:<Project_Name>.svc.id.goog[crossplane-system/<Kubernetes_Service_Account>]" \
--project <Project_Name>
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: workload-identity-runtimeconfig
spec:
serviceAccountTemplate:
metadata:
annotations:
iam.gke.io/gcp-service-account: <GCP_IAM_service_account_email>
name: <Kubernetes_service_account_name>
Apply the DeploymentRuntimeConfig
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-gcp-storage
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-gcp-storage:v2.1.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: workload-identity-runtimeconfig
Create a ProviderConfig
apiVersion: gcp.upbound.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
projectID: <Project_Name>
credentials:
source: InjectedIdentity
Kubernetes authentication
The Upbound Official Kubernetes Provider supports multiple authentication methods.
Kubernetes Upbound Identity
This method is only supported in control planes running on Upbound Cloud Spaces.
Use this method to interact with Upbound APIs using provider-kubernetes. Upbound Identity supports the following authentication methods with Upbound:
- A user's personal access token (PAT)
- A token generated from a robot
Create an access token
- Robot
- Personal Access Token
This method creates a Robot, the Upbound-equivalent of a service account, and uses its identity to authenticate and perform actions.
- Login to Upbound:
up login
- Create a robot:
up robot create "provider-kubernetes" --description="Robot used for authenticating to Upbound by provider-kubernetes"
- Create and store an access token for this robot as an environment variable:
export UPBOUND_TOKEN=$(up robot token create "provider-kubernetes" "provider-kubernetes-token" --file - | jq -r '.token')
Follow the jq installation guide if your machine doesn't include it by default.
- Assign the robot to a team and use Upbound RBAC to grant the team a role for permissions.
Create a personal access token and store it as an environment variable:
export UPBOUND_TOKEN="YOUR_API_TOKEN"
Generate a kubeconfig for Upbound APIs
Upbound APIs are Kubernetes-compatible. Generate a kubeconfig for the context you want to interact with:
Set the desired context path below depending on your use case. Generate a kubeconfig according to the token method you followed in the prior section.
- Robot
- User account
- Login to Upbound with the robot access token:
up login -t $UPBOUND_TOKEN
- Set your Upbound context:
up ctx org/space/group/control-plane
up ctx . -f - > upbound-context.yaml
- Login to Upbound:
up login
- Set your Upbound context:
up ctx org/space/group/control-plane
up ctx . -f - > upbound-context.yaml
Store the generated context as an environment variable:
export CONTROLPLANE_CONFIG=upbound-context.yaml
Create secrets
In the control plane where you've installed provider-kubernetes, store the tokens created in the earlier step as secrets:
kubectl -n crossplane-system create secret generic cluster-config --from-file=kubeconfig=$CONTROLPLANE_CONFIG
kubectl -n crossplane-system create secret generic upbound-credentials --from-literal=token=$UPBOUND_TOKEN
Create a ProviderConfig
apiVersion: kubernetes.crossplane.io/v1alpha1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
secretRef:
key: kubeconfig
name: cluster-config
namespace: crossplane-system
source: Secret
identity:
secretRef:
key: token
name: upbound-credentials
namespace: crossplane-system
source: Secret
type: UpboundTokens
Kubernetes Injected Identity
Use this method for a control plane to manage resources in itself using a cluster-admin role.
Create a ProviderConfig
apiVersion: kubernetes.crossplane.io/v1alpha1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: InjectedIdentity
Create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: provider-kubernetes
spec:
serviceAccountTemplate:
metadata:
name: provider-kubernetes
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: provider-kubernetes-cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: provider-kubernetes
namespace: crossplane-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Reference this DeploymentRuntimeConfig in the Provider:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-kubernetes
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-kubernetes:v1.2.0
runtimeConfigRef:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
name: provider-kubernetes
Kubernetes Injected Identity with Cloud Provider Credentials
Use this method to authenticate the Kubernetes provider to a remote cluster using cloud provider credentials in EKS, GKE, AKS, or Upbound Cloud Spaces with OIDC.
The provider supports the following identity types for authentication:
AWSWebIdentityCredentials: For EKS clusters using AWS IAM rolesGoogleApplicationCredentials: For GKE clusters using Google service accountsAzureServicePrincipalCredentials: For AKS clusters using Azure service principalsAzureWorkloadIdentityCredentials: For AKS clusters using Azure workload identityUpboundTokens: For Upbound APIs using Upbound authentication
This guide demonstrates the AWS Web Identity approach, which works in both Upbound Cloud Spaces (using Upbound OIDC) and when running directly in EKS (using EKS OIDC).
Create an AWS IAM Role
Create an AWS IAM Role with a Custom trust policy for the OIDC connector.
- Upbound Cloud Spaces
- Running in EKS
For control planes running in Upbound Cloud Spaces, create an IAM role in AWS with a trust policy that allows the provider running in your control plane to assume the role via Upbound's OIDC service.
-
Follow the AWS Upbound OIDC setup to add Upbound as an OpenID Connect provider in your AWS account if you haven't already.
-
Create an IAM role with the following trust policy. This policy establishes a federated trust relationship with Upbound's OIDC provider (
proidc.upbound.io) and restricts role assumption to only the specific provider in your control plane:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:oidc-provider/proidc.upbound.io"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"proidc.upbound.io:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com",
"proidc.upbound.io:sub": "mcp:$ORG/$CONTROL_PLANE_NAME*:provider:upbound-provider-kubernetes"
}
}
}
]
}
Replace the following values:
$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID: Your AWS account ID$ORG: Your Upbound organization name$CONTROL_PLANE_NAME: Your control plane name
The Federated principal references Upbound's OIDC provider, and the
Condition ensures only your specific provider can assume this role.
- Attach the necessary AWS permissions to this role (for example, permissions to access EKS clusters).
When running in EKS, you must first configure IRSA or EKS Pod Identity for the provider. This guide assumes you have already completed the IRSA or Pod Identity setup.
For providers running directly in EKS, use the EKS cluster OIDC provider. Follow the IRSA setup for creating the IAM role trust policy and configuring the provider's service account.
Configure target EKS cluster access
Configure your EKS cluster to allow the IAM role to access it.
Use one of the following methods:
- EKS Access Entries (recommended)
- aws-auth ConfigMap
Assign appropriate Kubernetes permissions (for example, system:masters group
for full access or create a custom Role/RoleBinding).
Configure the Provider
- Upbound Cloud Spaces
- Running in EKS
For control planes running in Upbound Cloud Spaces, create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig to inject the Upbound OIDC token and AWS credentials:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: aws-audience
spec:
deploymentTemplate:
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
proidc.cloud-spaces.upbound.io/audience: sts.amazonaws.com
spec:
containers:
- name: package-runtime
env:
- name: AWS_WEB_IDENTITY_TOKEN_FILE
value: /var/run/secrets/upbound.io/provider/token
- name: AWS_ROLE_ARN
value: arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ROLE_NAME
- name: AWS_REGION
value: $AWS_REGION
selector: {}
---
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-kubernetes
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-kubernetes:v1.2.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: aws-audience
Replace $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID, $ROLE_NAME, and $AWS_REGION with your values.
This assumes you have already configured IRSA or EKS Pod Identity for the provider-kubernetes package. The provider's service account must have the appropriate IAM role annotation.
For providers running directly in EKS with IRSA, install the provider with your IRSA DeploymentRuntimeConfig:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-kubernetes
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-kubernetes:v1.2.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: irsa-runtimeconfig
EKS automatically injects the web identity token when the service account has
the eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn annotation. Refer to the IRSA
section for the complete setup.
Create a kubeconfig Secret
Generate a kubeconfig for your EKS cluster using the AWS CLI:
aws eks update-kubeconfig \
--region $AWS_REGION \
--name $CLUSTER_NAME \
--profile $AWS_PROFILE \
--kubeconfig eks-kubeconfig.txt
Create a Secret containing the kubeconfig for your EKS cluster. Use an empty user configuration in the kubeconfig, as the provider reads AWS credentials from environment variables:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: cluster-config
type: Opaque
stringData:
kubeconfig: |
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: $CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY_DATA
server: https://$EKS_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT
name: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
contexts:
- context:
cluster: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
user: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
name: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
current-context: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
user: {}
Replace the following placeholders with values from your generated kubeconfig:
$CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY_DATA: The base64-encoded certificate authority data for your EKS cluster$EKS_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT: Your EKS cluster endpoint (for example,ABC123.gr7.us-west-2.eks.amazonaws.com)$EKS_CLUSTER_ARN: Your EKS cluster ARN (for example,arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-cluster)
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig that uses the Secret credentials and AWS Web Identity for authentication:
apiVersion: kubernetes.crossplane.io/v1alpha1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: cluster-config
key: kubeconfig
identity:
source: InjectedIdentity
type: AWSWebIdentityCredentials
Helm authentication
The Upbound Official Helm Provider supports multiple authentication methods for accessing Kubernetes clusters.
Helm Injected Identity with Cloud Provider Credentials
Use this method to authenticate the Helm provider to a remote cluster using cloud provider credentials in EKS, GKE, AKS, or Upbound Cloud Spaces with OIDC.
The provider supports the following identity types for authentication:
AWSWebIdentityCredentials: For EKS clusters using AWS IAM rolesGoogleApplicationCredentials: For GKE clusters using Google service accountsAzureServicePrincipalCredentials: For AKS clusters using Azure service principalsAzureWorkloadIdentityCredentials: For AKS clusters using Azure workload identity
This guide demonstrates the AWS Web Identity approach, which works in both Upbound Cloud Spaces (using Upbound OIDC) and when running directly in EKS (using EKS OIDC).
Create an AWS IAM Role
Create an AWS IAM Role with a Custom trust policy for the OIDC connector.
- Upbound Cloud Spaces
- Running in EKS
For control planes running in Upbound Cloud Spaces, create an IAM role in AWS with a trust policy that allows the provider running in your control plane to assume the role via Upbound's OIDC service.
-
Follow the AWS Upbound OIDC setup to add Upbound as an OpenID Connect provider in your AWS account if you haven't already.
-
Create an IAM role with the following trust policy. This policy establishes a federated trust relationship with Upbound's OIDC provider (
proidc.upbound.io) and restricts role assumption to only the specific provider in your control plane:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Federated": "arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:oidc-provider/proidc.upbound.io"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity",
"Condition": {
"StringLike": {
"proidc.upbound.io:aud": "sts.amazonaws.com",
"proidc.upbound.io:sub": "mcp:$ORG/$CONTROL_PLANE_NAME*:provider:upbound-provider-helm"
}
}
}
]
}
Replace the following values:
$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID: Your AWS account ID$ORG: Your Upbound organization name$CONTROL_PLANE_NAME: Your control plane name
The Federated principal references Upbound's OIDC provider, and the
Condition ensures only your specific provider can assume this role.
- Attach the necessary AWS permissions to this role (for example, permissions to access EKS clusters).
When running in EKS, you must first configure IRSA or EKS Pod Identity for the provider. This guide assumes you have already completed the IRSA or Pod Identity setup.
For providers running directly in EKS, use the EKS cluster OIDC provider. Follow the IRSA setup for creating the IAM role trust policy and configuring the provider's service account.
Configure target EKS cluster access
Configure your EKS cluster to allow the IAM role to access it.
Use one of the following methods:
- EKS Access Entries (recommended)
- aws-auth ConfigMap
Assign appropriate Kubernetes permissions (for example, cluster-admin role for
full access or create a custom Role/RoleBinding).
Configure the Provider
- Upbound Cloud Spaces
- Running in EKS
For control planes running in Upbound Cloud Spaces, create a DeploymentRuntimeConfig to inject the Upbound OIDC token and AWS credentials:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: DeploymentRuntimeConfig
metadata:
name: helm-aws-audience
spec:
deploymentTemplate:
spec:
template:
metadata:
annotations:
proidc.cloud-spaces.upbound.io/audience: sts.amazonaws.com
spec:
containers:
- name: package-runtime
env:
- name: AWS_WEB_IDENTITY_TOKEN_FILE
value: /var/run/secrets/upbound.io/provider/token
- name: AWS_ROLE_ARN
value: arn:aws:iam::$AWS_ACCOUNT_ID:role/$ROLE_NAME
- name: AWS_REGION
value: $AWS_REGION
selector: {}
---
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-helm
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-helm:v1.1.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: helm-aws-audience
Replace $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID, $ROLE_NAME, and $AWS_REGION with your values.
This assumes you have already configured IRSA or EKS Pod Identity for the provider-helm package. The provider's service account must have the appropriate IAM role annotation.
For providers running directly in EKS with IRSA, install the provider with your IRSA DeploymentRuntimeConfig:
apiVersion: pkg.crossplane.io/v1
kind: Provider
metadata:
name: provider-helm
spec:
package: xpkg.upbound.io/upbound/provider-helm:v1.1.0
runtimeConfigRef:
name: irsa-runtimeconfig
EKS automatically injects the web identity token when the service account has
the eks.amazonaws.com/role-arn annotation. Refer to the IRSA
section for the complete setup.
Create a kubeconfig Secret
Generate a kubeconfig for your EKS cluster using the AWS CLI:
aws eks update-kubeconfig \
--region $AWS_REGION \
--name $CLUSTER_NAME \
--profile $AWS_PROFILE \
--kubeconfig eks-kubeconfig.txt
Create a Secret containing the kubeconfig for your EKS cluster. Use an empty user configuration in the kubeconfig, as the provider reads AWS credentials from environment variables:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: helm-cluster-config
type: Opaque
stringData:
kubeconfig: |
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: $CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY_DATA
server: https://$EKS_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT
name: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
contexts:
- context:
cluster: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
user: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
name: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
current-context: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: $EKS_CLUSTER_ARN
user: {}
Replace the following placeholders with values from your generated kubeconfig:
$CERTIFICATE_AUTHORITY_DATA: The base64-encoded certificate authority data for your EKS cluster$EKS_CLUSTER_ENDPOINT: Your EKS cluster endpoint (for example,ABC123.gr7.us-west-2.eks.amazonaws.com)$EKS_CLUSTER_ARN: Your EKS cluster ARN (for example,arn:aws:eks:us-west-2:123456789012:cluster/my-cluster)
Create a ProviderConfig
Create a ProviderConfig that uses the Secret credentials and AWS Web Identity for authentication:
apiVersion: helm.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: ProviderConfig
metadata:
name: default
spec:
credentials:
source: Secret
secretRef:
namespace: crossplane-system
name: helm-cluster-config
key: kubeconfig
identity:
source: InjectedIdentity
type: AWSWebIdentityCredentials